BIP | Blended Intensive Programme
Blended Intensive Programme (BIP) in Prague
Planning and economics of cities
2.3. – 13. 3. 2026
3ECTS
IN PARTNERSHIP WITH:
Polytechnic University of Lisbon, ISCAL- Lisbon Accounting and Business School, Portugal
Bratislava University of Economics and Business, Faculty of Economics and Finance, Slovakia
ISCTE – Lisbon University Institute, School of Social Sciences, Portugal
Prague University of Economics and Business – responsible persons and teachers:
Dr. Barbora Růžičková, Academic Coordinator and Administrative Coordinator
Dr. Martin Lukavec – teacher
Dr. Hana Černá Silovská – teacher
Language of instruction: English
For students: students of economics, public policy, and regional development.
Overview and scope
The Blended Intensive Programme Planning and Economics of Cities bridges the fields of urban planning, economics, and public policy. It focuses on understanding how spatial decisions interact with market forces, infrastructure, and local governance. Students will learn how to model, analyse, and evaluate urban structures using both theoretical frameworks and applied tools. The programme combines lectures, seminars, and workshops, integrating economic theory with real-world urban strategy design and data-based analysis.
Outputs
- Improved understanding of urban-economic mechanisms shaping modern cities
- Practical skills in land-price and density gradient modelling using GIS data
- Experience with fiscal analysis of local governments and public investment evaluation
- Development of calibrated urban simulation models (Alonso-Muth-Mills, RELU-TRAN)
- Policy briefs and group presentations translating analytical results into actionable recommendations
- Strengthened international cooperation among participating universities and interdisciplinary teams
Teaching Methodologies
- Thematic lectures providing conceptual and theoretical foundations
- Interactive seminars and guided debates encouraging critical reflection and application
- Case-study analysis and research projects involving real urban data and stakeholder perspectives
- Data-driven analytical labs using GIS and regression tools for spatial analysis
- Simulation workshops modelling policy scenarios and their socio-economic impacts
- Policy-evaluation clinics focused on translating analytical outcomes into policy advice
Evaluation
Student performance in the programme will be evaluated on a pass/fail basis.
Students will be assessed based on:
- Active participation and attendance – compulsory in both the virtual and physical parts of the programme.
- Individual and group assignments – analytical exercises, case studies, and simulation outputs.
- Continuous feedback during discussions, workshops, and project work.
Students who pass will receive Certificate of Completion.
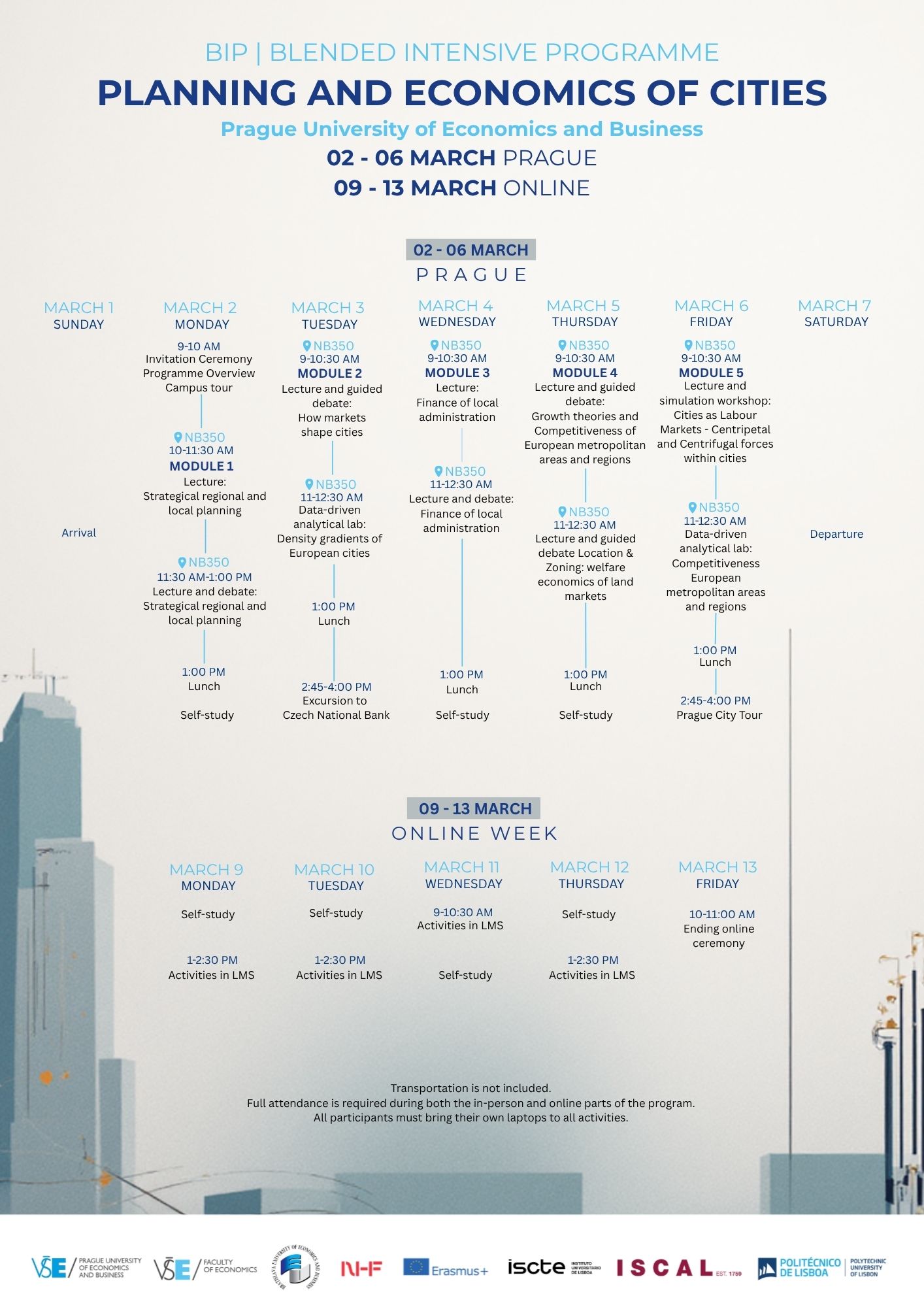
Modules
PROGRAMME OVERVIEW AND WELCOME (1 hour)
This part aims to welcome the participants, introducing the main concepts and tools to be used at the BIP, providing them with tutorials aimed at clarifying any questions or doubts.
Duration: 1 hour
Module 1: STRATEGICAL REGIONAL AND LOCAL PLANNING. IMPORTANCE OF REGIONAL AND SPATIAL PLANNING IN CITIES´ DEVELOPMENT (12 hours) – Dr. Černá Silovská
This module focuses on understanding the key principles, processes, and tools used in regional and spatial planning. It highlights the importance of coordinated planning for sustainable urban and regional development, emphasizing how strategic decision-making influences economic growth, social cohesion, and environmental balance. Students will explore how regional and local planning shape cities’ development, address spatial inequalities, and support the creation of resilient, well-organized, and livable urban environments.
6h lectures/guided debate during the physical and virtual components involving case studies, team works, discussions. Plus 6 hours of asynchronous self-study (readings, tasks, quiz etc.).
Module 2: HOW MARKETS SHAPE CITIES + ZONING POLICIES (15 hours) – Dr. Lukavec
In this module, you will explore how cities grow and function as living expressions of market forces rather than as outcomes of urban design alone. You will examine how land prices, density, and building patterns emerge from millions of individual choices shaped by accessibility and competition for space. The module also investigates how zoning policies influence these dynamics—sometimes helping to manage externalities, but often distorting market signals and driving up costs. Through global examples, you will consider instances of planning supporting development of cities, but also how over-regulation can freeze development, worsen inequality, and hinder urban creativity.
Physical part: Thematic lecture block & Interactive seminar & Data-driven analytical lab: 6 hours
Self study: readings, podcasts: 6 hours
Online part: online-lecture, readings, podcasts + discussion questions: 3 hours
Module 3: FINANCE OF LOCAL ADMINISTRATION. HOW SETTLEMENT AND ADMINISTRATIVE STRUCTURES AFFECT LOCAL FINANCE. FISCAL DECENTRALIZATION AND TAX SYSTEM (12 hours) – Dr. Černá Silovská
This module explores how settlement patterns and administrative structures influence the financial management of local governments. It examines the relationship between decentralization, fiscal autonomy, and the tax system, providing insights into how local authorities generate and allocate resources. Through case studies, students will analyze different models of local finance, understanding the challenges and opportunities in ensuring efficient, transparent, and sustainable financial governance at the local level.
6h lectures/guided debate during the physical and virtual components involving case studies, team works, discussions. Plus 6 hours of asynchronous self-study (readings, tasks, quiz etc.).
Module 4: GROWTH THEORIES AND COMPETITIVENESS OF EUROPEAN METROPOLITAN AREAS AND REGIONS (15 hours) – Dr. Lukavec
This module introduces the main theories that explain why some cities and regions grow faster than others. You will study how agglomeration economies—such as shared labour markets, knowledge spillovers, and innovation networks—drive productivity and competitiveness. The module compares different growth patterns across Europe, showing how large metropolitan areas benefit from scale, yet smaller cities remain important as specialised hubs. You will discuss how policies that restrict mobility or attempt to “balance” growth can backfire by reducing efficiency, and how regional competitiveness depends on enabling openness, connectivity, and flexible land use within integrated urban systems.
Physical part: Thematic lecture block & guided debate: 6 hours
Self study: readings, podcasts: 6 hours
Online part: online-lecture, readings, podcasts + discussion questions: 3 hours
Module 5: CITIES AS LABOUR MARKETS – CENTRIPETAL AND CENTRIFUGAL FORCES WITHIN CITIES (15 hours) – Dr. Lukavec
In this module, you will learn to view cities as labour markets—places where people and firms interact through the exchange of skills and opportunities. You will examine the forces that pull activity toward the city centre, such as knowledge exchange and proximity to services, and those that push it outward, including congestion, high rents, and improved transport networks. Using examples from global cities, you will trace how metropolitan areas evolve from single centres into networks of sub-centres as they expand. The module focuses on how accessibility, affordability, and efficient transport systems sustain productive labour markets and prevent cities from fragmenting into disconnected, unequal spaces.
Physical part: Lecture and simulation workshop, Data-driven analytical lab: 6 hours
Self study: readings, podcasts: 6 hours
Online part: online-lecture, readings, podcasts + discussion questions: 3 hours
SOCIAL ACTIVITIES (4 hours):
Explore the Czech National Bank
Prague City Tour